State of the Climate in Asia 2024
<p>The World Meteorological Organization’s State of the Climate in Asia 2024 report warns that the region is warming nearly twice as fast as the global average, driving more extreme weather and posing
<p>The World Meteorological Organization’s State of the Climate in Asia 2024 report warns that the region is warming nearly twice as fast as the global average, driving more extreme weather and posing
The highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N1 virus that emerged in southern China in the mid-1990s has in recent years evolved into the first HPAI panzootic.
In Africa, hard-hit by HIV, the proportion of TB drug-resistance is no less alarming. In former Soviet Union, almost half of all TB cases are resistant to at least one anti-TB drug -Bobby Ramakant
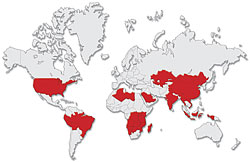
plague cases are on the rise and are afflicting countries more frequently than before. A who report says there were around 1,900 cases worldwide in 2002, which increased to 2,100 cases in 2003. In
Disease remains a "stubborn threat' to public health, says report Responsible for almost 10 per cent of AIDS-related deaths India loses 100 million productive workdays every year because of TB
The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation has called on the oil-producing countries of the Middle East to invest more of their oil windfalls in developing agriculture in their region, in or
There are two broad categories of marginal-quality water: wastewater generated by the domestic, commercial, and industrial sectors; and saline water from agricultural drainage systems, surface runoff, or pumped from overexploited aquifers. Millions of small-scale farmers around the world irrigate with marginal-quality water, often because they have no alternative.
After 30 years of dynamic growth and substantial poverty reduction in Asia, do agriculture and rural development still have a role to play in that region?
This article argues that waste management and recycling have become regional or international issues; they can no longer be considered only in a national context. The regionalization or internationalization of waste and recycling issues is caused in large part by the steady advance of economic integration, especially increasing trade and investment flows resulting from trade and investment liberalization.
The problems relating to mounting solid waste are fast acquiring gigantic proportions in the developing countries of Asia. Most of the countries, nevertheless, continue to primarily focus on achieving high economic growth and pay scant attention to waste management. This article takes a detailed look at the inadequacies of waste management in Asia and underscores the need for greater international engagement in tackling the menace.
This dossier is located within the context of increasing global discontent and community protest against interventions of International Financial Institutions (IFIs) in the developing world. It specifically presents a questioning and critique of their operations in tourism.